Comprehensive Guide to Elbow Anatomy and Conditions
Guía Integral sobre el Codo: Anatomía y Condiciones
The “funny bone” is inside the elbow. But as anyone who has ever suffered from elbow pain, injuries, or conditions, there’s nothing funny about elbow problems. Elbow problems can cause tremendous discomfort and pain whether you’re awake or asleep, and can also significantly impact your ability to lift even small objects.
To help you discuss elbow conditions and treatment options with your surgeon, here’s a breakdown of the anatomy of the elbow.
El “hueso de la risa” está dentro del codo, pero quienes han sufrido dolor, lesiones o problemas en el codo saben que no tiene nada de gracioso. Los problemas en el codo pueden causar dolor intenso, incluso al dormir, y afectar la capacidad de levantar objetos, incluso pequeños.
Para ayudarte a comprender mejor tu condición y hablar con tu cirujano sobre opciones de tratamiento, aquí te presentamos una descripción detallada de la anatomía del codo.
- Anatomy Anatomía
- Conditions Condiciones
- Procedures Cirugías
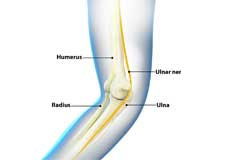
Elbow Anatomy
The elbow is a complex joint that helps in bending or straightening of the arm, and lifting or moving objects. The elbow joint is formed at the junction of three bones:
- The humerus forms the upper portion of the joint, and divides into two bony protrusions, the medial and lateral epicondyles.
- The ulna is the larger bone of the forearm located on the inner surface of the joint, and articulates with the humerus.
- The radius is the smaller bone of the forearm, and is situated on the outer surface of the joint, allows movement with the humerus, and helps the forearm to rotate.
Joints of the elbow
The elbow consists of three joints:
- The humeroulnar joint is formed between the humerus and ulna, and allows flexion and extension of the arm.
- The humeroradial joint is formed between the radius and humerus, and allows movements like flexion, extension, supination, and pronation.
- The radioulnar joint is formed between the ulna and radius bones, and allows rotation of the lower arm.
Articular cartilage lines the articulating regions of the humerus, radius, and ulna. It is a thin, tough, flexible and slippery surface that acts as a shock absorber and cushion to reduce friction between the bones. The cartilage is lubricated with synovial fluid, which further enables the smooth movement of the bones.
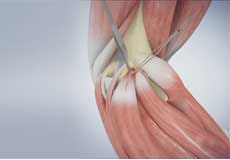
Muscles of the Elbow
There are several muscles extending across the elbow joint that help in various movements:
- Biceps brachii enabling flexion of the arm.
- Triceps brachii extends the arm and fixes the elbow during fine movements.
- Brachialis flexes the elbow towards the body.
- Brachioradialis straightens and pulls the arm at the elbow.
- Pronator teres helps to turn the palm facing backward.
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis helps in movement of the hand
- Extensor digitorum helps in movement of the fingers
Ligaments of the Elbow
The ligaments connect the bones of the elbow. The most important ligaments of the elbow joint are the:
- Medial or ulnar collateral ligament: Comprised of triangular bands of tissue on the inner side of the elbow joint
- Lateral or radial collateral ligament: A thin band of tissue on the outer side of the elbow joint
- Annular ligament: Group of fibers that surround the radial head, and hold the ulna and radius tightly in place during movement of the arm
Together, the medial and lateral ligaments are the main source of stability and hold the humerus and ulna tightly in place during movement of the arm.
Tendons of the Elbow
The tendons connect the muscles of the elbow to the bones. The tendons that surround the elbow joint are:
- Biceps tendon attaches the biceps muscle to the radius, allowing the elbow to bend
- Triceps tendon attaches the triceps muscle to the ulna, allowing the elbow to straighten
Nerves of the Elbow
The main nerves of the elbow joint are the ulnar, radial and median nerves. These nerves transfer signals from the brain to the muscles that aid in elbow movements. They also carry sensory signals such as touch, pain, and temperature back to the brain.
Blood Vessels Supplying the Elbow
The brachial artery travels across the inside of the elbow to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the hand.
Injuries to the elbow are no laughing matter. Let us help you solve your elbow problems and conditions, and get your smile back.
Anatomía del Codo
El codo es una articulación compleja que permite doblar o estirar el brazo, así como levantar y mover objetos. Está formada por la unión de tres huesos:
- Húmero: Forma la parte superior de la articulación y se divide en dos protuberancias óseas: el epicóndilo medial y el epicóndilo lateral.
- Cúbito (ulna): Es el hueso más grande del antebrazo, ubicado en la parte interna de la articulación, y se articula con el húmero.
- Radio: Es el hueso más pequeño del antebrazo, ubicado en la parte externa de la articulación, permite el movimiento con el húmero y ayuda a que el antebrazo gire.
Articulaciones del Codo
El codo está compuesto por tres articulaciones principales:
- Articulación húmero-cubital: Entre el húmero y el cúbito, permite la flexión y extensión del brazo.
- Articulación húmero-radial: Entre el radio y el húmero, permite movimientos como flexión, extensión, supinación y pronación.
- Articulación radio-cubital: Entre el radio y el cúbito, permite la rotación del antebrazo.
El cartílago articular cubre las áreas de contacto de los huesos, funcionando como amortiguador y reduciendo la fricción. Además, el líquido sinovial lubrica la articulación, facilitando el movimiento suave de los huesos.
Músculos del Codo
Los músculos que rodean el codo permiten diversos movimientos:
- Bíceps braquial: Flexiona el brazo.
- Tríceps braquial: Extiende el brazo y estabiliza el codo en movimientos precisos.
- Braquial: Flexiona el codo hacia el cuerpo.
- Braquiorradial: Ayuda a enderezar y retraer el brazo.
- Pronador redondo: Permite girar la palma hacia abajo.
- Extensor radial corto del carpo: Facilita el movimiento de la mano.
- Extensor común de los dedos: Permite el movimiento de los dedos.
Ligamentos del Codo
Los ligamentos conectan los huesos del codo y proporcionan estabilidad:
- Ligamento colateral medial (cubital): Banda triangular de tejido ubicada en la parte interna del codo.
- Ligamento colateral lateral (radial): Banda delgada ubicada en la parte externa.
- Ligamento anular: Rodea la cabeza del radio y mantiene firmemente unidos el cúbito y el radio durante los movimientos.
Estos ligamentos son esenciales para la estabilidad y el correcto funcionamiento del codo.
Tendones del Codo
Los tendones conectan los músculos a los huesos:
- Tendón del bíceps: Une el bíceps al radio, permitiendo la flexión del codo.
- Tendón del tríceps: Une el tríceps al cúbito, permitiendo la extensión del codo.
Nervios y Vasos Sanguíneos
Los nervios principales del codo son el cubital, radial y mediano. Estos transmiten señales motoras y sensoriales, incluyendo tacto, dolor y temperatura.
Vasos sanguíneos
La arteria braquial suministra sangre oxigenada desde el corazón al brazo, codo y mano.
Las lesiones de codo no son cosa de risa. Permítanos ayudarle a solucionar sus problemas y afecciones de codo y a recuperar su sonrisa.
Elbow Pain
The elbow is a hinge joint made up of 3 bones - the humerus, radius, and ulna. The bones are held together by ligaments to provide stability to the joint. Muscles and tendons move the bones around each other and help in performing various movements.
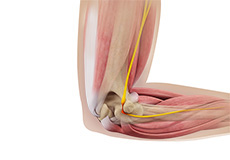
Ulnar Nerve Neuropathy
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is the entrapment or compression of the ulnar nerve causing impairment of its function.
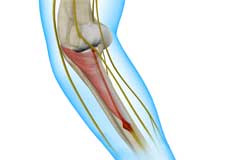
Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Radial tunnel syndrome is a painful condition caused by pressure on the radial nerve of the forearm. The entrapment or compression occurs frequently in the proximal forearm in the radial tunnel; a narrow space formed by muscles, bone, and tendon near the elbow joint.

Throwing Injuries
An athlete uses an overhand throw to achieve greater speed and distance. Repeated throwing in sports such as baseball and basketball can place a lot of stress on the joints of the arm, and lead to weakening and ultimately, injury to the structures in the elbow. These overuse injuries may include:

Hyperextension Injury Of The Elbow
Hyperextension injury of the elbow occurs when the elbow joint is bent beyond its normal range of motion, causing damage to the bones and ligaments of the elbow. It may also cause elbow dislocation. The condition is more common in tennis, football, weight-lifting and contact sports.
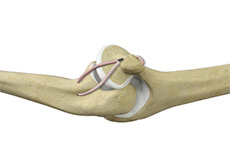
Lateral Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries (Elbow)
A ligament is a band of elastic, tough fibrous connective tissue around a joint. It attaches bone to bone, supports and holds them together and limits the joint's movement.
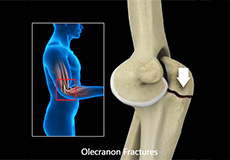
Elbow Fractures
The arm in the human body is made up of three bones that join to form a hinge joint called the elbow. The upper arm bone or humerus connects from the shoulder to the elbow to form the top of the hinge joint. The lower arm or forearm consists of two bones, the radius and the ulna. These bones connect the wrist to the elbow forming the bottom portion of the hinge joint.

Mid-shaft Humerus Fracture
A mid-shaft humerus fracture is a common type of humerus fracture that occurs along the mid-section of the humerus or upper arm bone.
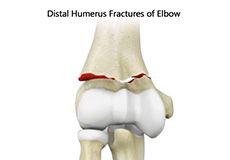
Distal Humerus Fractures Of The Elbow
The elbow is a region between the upper arm and forearm. The elbow joint is made up of 3 bones. The distal (lower) end of the humerus bone in the upper arm joins with the radius and ulna bones in the forearm to form the elbow joint. The elbow joint is very important for the movement of your arms and for coordination of daily activities.
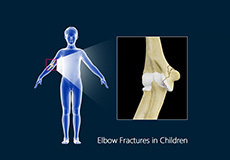
Elbow Fractures In Children
The arm in the human body is made up of three bones that join to form a hinge joint called the elbow. The upper arm bone or humerus connects from the shoulder to the elbow to form the top of the hinge joint. The lower arm or forearm consists of two bones, the radius, and the ulna.
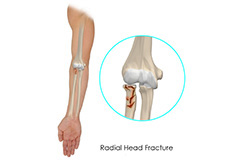
Radial Head Fractures Of The Elbow
The arm in the human body is made up of three bones that join to form a hinge joint called the elbow. The upper arm bone or humerus connects from the shoulder to the elbow to form the top of the hinge joint. The lower arm or forearm consists of two bones, the radius, and the ulna. These bones connect the wrist to the elbow forming the bottom portion of the hinge joint.

Post-traumatic Stiffness (Elbow)
Medically, stiffness is difficulty moving a joint due to the loss of the joint's range of motion caused by an injury (trauma) or a disorder.
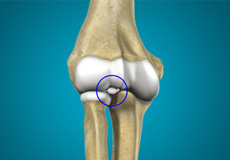
Loose Bodies In The Elbow
Your elbow is a joint made up of three bones held together by muscles, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. It is both a hinge and pivot joint allowing you to bend and rotate your elbow freely. Loose bodies in your elbow are small pieces of bone or cartilage that have broken off and are lying or floating free within the joint. They can make elbow movement such as bending or rotation difficult.
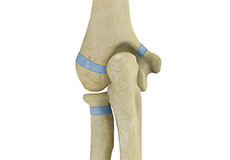
Little League Elbow
Little league elbow, also called medial apophysitis, is an overuse condition that occurs when there is overstress or injury to the inside portion of the elbow. It is commonly seen in children involved in sports activities that require repetitive throwing such as baseball.
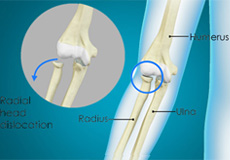
Nursemaid's Elbow
The elbow is a complex joint formed by the articulation of three bones - the humerus, radius, and ulna. The elbow joint helps in bending or straightening of the arm to 180 degrees and lifting or moving objects.
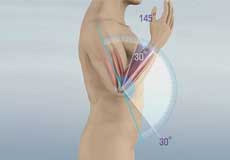
Elbow Contracture
Elbow contracture refers to a stiff elbow with a limited range of motion. It is a common complication following elbow surgery, fractures, dislocations, and burns.
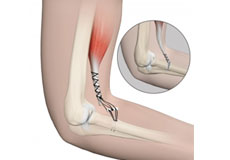
Distal Biceps Repair
The biceps is a large muscle located in the front of your upper arm and runs from the shoulder to the elbow joint. It is attached to the bones of the shoulder and elbow by tendons. The distal biceps is the area where the biceps is attached to the forearm bone in the elbow.

Dolor de Codo
El codo es una articulación en bisagra formada por 3 huesos: el húmero, el radio y el cúbito. Los huesos se mantienen unidos por ligamentos que proporcionan estabilidad a la articulación. Los músculos y tendones mueven los huesos entre sí y ayudan a realizar varios movimientos.

Neuropatía del Nervio Cubital
La neuropatía del nervio cubital es la compresión o atrapamiento del nervio cubital que provoca un deterioro en su función.

Síndrome del Túnel Radial
El síndrome del túnel radial es una condición dolorosa causada por la presión sobre el nervio radial del antebrazo. El atrapamiento o la compresión ocurre con frecuencia en la parte proximal del antebrazo, en el túnel radial, un espacio estrecho formado por músculos, hueso y tendones cerca de la articulación del codo.

Lesiones por Lanzamiento
Un atleta utiliza un lanzamiento por encima de la cabeza para lograr mayor velocidad y distancia. Los lanzamientos repetitivos en deportes como el béisbol y el baloncesto pueden ejercer mucha presión sobre las articulaciones del brazo y provocar debilitamiento y, en última instancia, lesiones en las estructuras del codo. Estas lesiones por uso excesivo pueden incluir:

Lesión por Hiperextensión del Codo
La lesión por hiperextensión del codo ocurre cuando la articulación del codo se dobla más allá de su rango normal de movimiento, causando daño en los huesos y ligamentos del codo. También puede provocar una dislocación del codo. Esta condición es más común en deportes como el tenis, el fútbol, el levantamiento de pesas y los deportes de contacto.

Lesiones del Ligamento Colateral Cubital Lateral (LUCL) del Codo
Un ligamento es una banda de tejido conectivo fibroso, elástico y resistente que rodea una articulación. Su función es unir hueso con hueso, proporcionar soporte, mantenerlos unidos y limitar el movimiento de la articulación.

Fracturas del Codo
El brazo humano está compuesto por tres huesos que se unen para formar una articulación de bisagra llamada codo. El hueso del brazo superior (húmero) conecta el hombro con el codo y forma la parte superior de la articulación. El antebrazo está formado por dos huesos, el radio y la ulna (cúbito), que conectan la muñeca con el codo, formando la parte inferior de la bisagra.

Fractura Diafisaria del Húmero
Una fractura diafisaria del húmero es un tipo común de fractura que ocurre a lo largo de la sección media del húmero, también conocido como hueso del brazo superior.

Fracturas del Húmero Distal del Codo
El codo es la región entre el brazo superior y el antebrazo. La articulación del codo está formada por tres huesos: el extremo distal (inferior) del húmero en el brazo superior se une con el radio y el cúbito en el antebrazo para formar la articulación del codo. Esta articulación es esencial para el movimiento de los brazos y la coordinación de actividades diarias.

Fracturas de Codo en Niños
El brazo en el cuerpo humano está compuesto por tres huesos que se unen para formar una articulación en bisagra llamada codo. El hueso del brazo superior o húmero conecta desde el hombro hasta el codo para formar la parte superior de la articulación en bisagra. El brazo inferior o antebrazo está compuesto por dos huesos, el radio y el cúbito.

Fracturas de Cabeza Radial del Codo
El brazo en el cuerpo humano está compuesto por tres huesos que se unen para formar una articulación en bisagra llamada codo. El hueso del brazo superior o húmero conecta desde el hombro hasta el codo para formar la parte superior de la articulación en bisagra. El brazo inferior o antebrazo está compuesto por dos huesos, el radio y el cúbito. Estos huesos conectan la muñeca con el codo formando la parte inferior de la articulación en bisagra.

Rigidez Postraumática (Codo)
Médicamente, la rigidez es la dificultad para mover una articulación debido a la pérdida del rango de movimiento causada por una lesión (trauma) o un trastorno.

Cuerpos Sueltos en el Codo
El codo es una articulación formada por tres huesos mantenidos juntos por músculos, ligamentos, tendones y cartílago. Es una articulación de bisagra y pivote que permite doblar y rotar el codo libremente. Los cuerpos sueltos en el codo son pequeños fragmentos de hueso o cartílago que se han desprendido y se encuentran sueltos o flotando dentro de la articulación. Estos pueden dificultar el movimiento del codo, como doblarlo o girarlo.

Codo de Pequeña Liga
El codo de pequeña liga, también llamado apofisitis medial, es una condición por uso excesivo que ocurre cuando hay sobreesfuerzo o lesión en la parte interna del codo. Es común en niños que participan en deportes que requieren lanzamientos repetitivos, como el béisbol.

Codo de Niñera
El codo es una articulación compleja formada por la articulación de tres huesos: el húmero, el radio y el cúbito. La articulación del codo ayuda a doblar o enderezar el brazo hasta 180 grados y levantar o mover objetos.

Contractura del Codo
ElLa contractura del codo se refiere a un codo rígido con un rango de movimiento limitado. Es una complicación común después de una cirugía de codo, fracturas, dislocaciones y quemaduras.

Reparación del Bíceps Distal
El bíceps es un músculo grande ubicado en la parte frontal de la parte superior del brazo y se extiende desde el hombro hasta la articulación del codo. Está unido a los huesos del hombro y el codo mediante tendones. El bíceps distal es el área donde el bíceps se une al hueso del antebrazo en el codo.
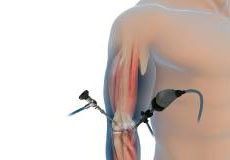
Elbow Arthroscopy
The elbow is a complex hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones - humerus, radius and ulna. The upper arm bone or humerus connects the shoulder to the elbow forming the upper portion of the hinge joint.
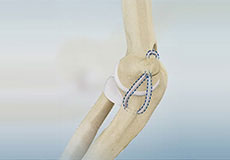
Ucl Reconstruction (Tommy John Surgery)
Commonly called Tommy John surgery, this procedure involves reconstructing a damaged ligament on the inside of the elbow called the ulnar or medial collateral ligament with a tendon graft obtained from your own body or a donor.
Golfer's Elbow Surgery
Golfer's elbow is a condition associated with pain on the inside of the elbow where tendons of your forearm attach to the bony prominence (medial epicondyle). It is also called medial epicondylitis and is caused by injury or irritation to the tendons which can become painful and swollen.
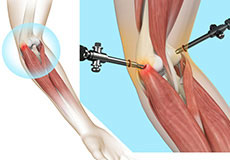
Tennis Elbow Surgery
The elbow is a joint made up of three bones: the upper arm bone, the humerus, and the two forearm bones, the radius and ulna. The lower end of the humerus has bony bumps called epicondyles that serve as sites of attachment for major tendons and muscles that help in arm movement.
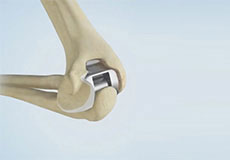
Total Elbow Replacement
The arm in the human body is made up of three bones that join to form a hinge joint called the elbow. The upper arm bone or humerus connects from the shoulder to the elbow to form the top of the hinge joint. The lower arm or forearm consists of two bones, the radius, and the ulna.

Revision Elbow Replacement
Revision elbow replacement is a surgery performed to replace a loose or worn out initial elbow replacement. Typically, cemented semi-constrained prostheses are used for revision elbow replacement.
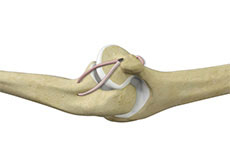
Elbow Ligament Reconstruction
The elbow is a complex joint of the upper limb formed by the articulation of the long bone of the upper arm or humerus and the two bones of the forearm, namely, radius and ulna. It is one of the important joints of the upper limb and is involved in basic movements such as flexion and extension of the upper limb and rotation of the forearm.

Arthroscopic Debridement Of The Elbow
Arthroscopic debridement of the elbow is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an arthroscope, a special tube-like instrument fitted with a camera and a light source, is inserted into the elbow through a tiny keyhole skin incision to identify and remove nonviable tissue and foreign debris from inside the elbow joint.

Cubital Tunnel Release (Ulnar Nerve Decompression))
Cubital tunnel syndrome is a condition characterized by compression of the ulnar nerve in an area of the elbow called the cubital tunnel. The ulnar nerve travels down the back of the elbow behind the bony bump called the medial epicondyle, and through a passageway called the cubital tunnel.

Endoscopic Cubital Tunnel Release
Endoscopic cubital tunnel release is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to decompress the ulnar nerve for the treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome. Endoscopic refers to the surgery being performed utilizing an endoscope - a thin, flexible fiber-optic tube with a camera, light, magnifying lens, and a port to pass tiny surgical instruments.
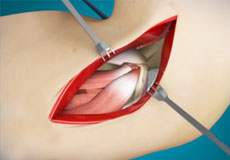
Open Elbow Surgery
Open elbow surgery is an operative procedure performed to treat certain conditions of your elbow through a large, open cut (incision) in the skin using a scalpel.
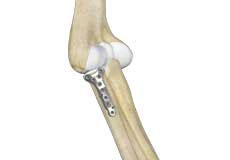
Radial Head Orif And Replacement
Radial Head Orif And Replacements are swellings that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of wrists or hands. They can be found either at the top of the wrist, palm side of the wrist, end joint of a finger or at the base of a finger.
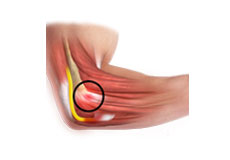
Common Extensor Tendon Origin Repair
The common extensor tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (long bone in the upper arm) at the elbow. Rupture or tear of the common extensor tendon is the most common acute tendon injury of the elbow.
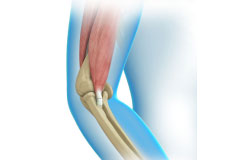
Elbow Tendon And Ligament Repair
The elbow is a complex joint of the upper limb formed by the articulation of the long bone of the upper arm or humerus and the two bones of the forearm, namely, radius and ulna. It is one of the important joints of the upper limb and is involved in basic movements such as flexion and extension of the upper limb and rotation of the forearm.
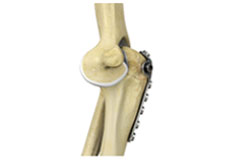
Elbow Fracture Reconstruction
Elbow fracture reconstruction is a surgical procedure employed to repair and restore the appearance and full function of a damaged elbow caused by severe trauma or injury. This may include repairing damaged structures or replacing missing or damaged structures with adjoining skin, muscles, ligaments, tendons, bones, or nerves to restore the appearance and function.
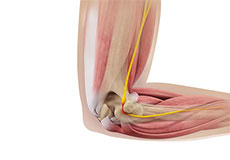
Ulnar Nerve Transposition
The ulnar nerve is one of the 3 main nerves in the arm that travels down from the neck through a bony protuberance inside the elbow (medial epicondyle), under the muscles of the forearm and down the hand on the side of the palm, towards the little finger.
Ulnar Nerve Release
Ulnar nerve release, also known as ulnar nerve decompression, is a surgical procedure to treat a medical condition called ulnar nerve entrapment or cubital tunnel syndrome.
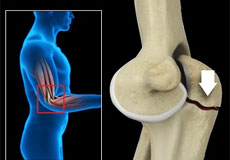
Orif Of The Distal Humerus Fractures
A distal humerus fracture is a condition that occurs when there is a break in the lower end of the humerus bone that commonly occurs as a result of severe trauma. Fracture of the distal humerus can affect the movement and function of your arm as well as your work and activities of daily living.
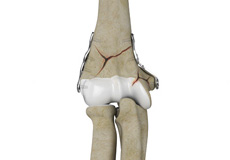
Orif Of The Olecranon Fractures
Olecranon fractures are described as a break in the bony tip of the elbow that sticks out when you bend your arm. A fracture of the olecranon bone can be very painful and make motion of the elbow difficult or impossible. This kind of fracture is common and normally happens in isolation (with no other injuries involved).

Orif Of The Coronoid Fractures
Coronoid fractures are a break in the coronoid process of the ulna due to trauma or injury. A coronoid fracture of the ulna is a complex intraarticular fracture that is difficult to expose due to complex surrounding anatomical structures.

Orif Proximal Humerus Fracture
A proximal humerus fracture is a break in the upper arm bone near the shoulder joint. This type of fracture can severely affect the shoulder joint and immediate medical attention is required in order to preserve shoulder function.

Non-union Surgery (Elbow)
Non-union is the failure of a broken or fractured bone to heal properly even after appropriate treatment.

Ulnar Collateral Ligament (Ucl) Repair With Internal Brace
UCL repair with an internal brace is a surgery that involves the use of collagen-coated tape (internal brace) surgically placed at the site of the damaged UCL ligaments. It provides better resistant and a faster recovery compared to traditional reconstruction surgery that involves the use of graft tissue from your body.

Artroscopia de Codo
El codo es una articulación compleja de bisagra formada por la articulación de tres huesos: húmero, radio y cúbito. El codo se mantiene en su lugar con el soporte de varios tejidos blandos, incluyendo cartílago, tendones, ligamentos, músculos, nervios, vasos sanguíneos y bursas.

Reconstrucción del UCL (Cirugía Tommy John)
Comúnmente llamada cirugía Tommy John, este procedimiento implica reconstruir un ligamento dañado en el interior del codo llamado ligamento colateral ulnar o medial con un injerto de tendón obtenido de su propio cuerpo o de un donante.

Cirugía de Codo de Golfista
El codo de golfista es una condición asociada con dolor en la parte interna del codo donde los tendones del antebrazo se insertan en la prominencia ósea (epicóndilo medial). También se llama epicondilitis medial y es causada por lesión o irritación de los tendones, que pueden volverse dolorosos e inflamados.

Cirugía de Codo de Tenista
El codo es una articulación formada por tres huesos: húmero, radio y cúbito. El extremo inferior del húmero tiene prominencias óseas llamadas epicóndilos, donde se insertan tendones y músculos que ayudan en el movimiento del brazo. La prominencia externa es el epicóndilo lateral, donde se insertan tendones y músculos que extienden los dedos y la muñeca.

Reemplazo Total de Codo
Cuando el cartílago articular del codo se desgasta, los extremos óseos rozan entre sí causando dolor, hinchazón, rigidez y limitación funcional. Puede deberse a lesiones o desgaste por edad.

Reemplazo de Codo de Revisión
El reemplazo de codo de revisión es una cirugía realizada para reemplazar un reemplazo de codo inicial suelto o desgastado. Generalmente se utilizan prótesis semi-constrainadas cementadas para el reemplazo de codo de revisión.

Reconstrucción de Ligamentos del Codo
El codo es una articulación compleja del miembro superior involucrada en movimientos básicos como flexión, extensión y rotación. Debido a su uso constante en la vida diaria, el codo es frecuentemente el sitio de lesiones y condiciones comunes, incluyendo: codo de tenista, codo de golfista, esguinces, rupturas y traumas.

Desbridamiento Artroscópico del Codo
Es un procedimiento quirúrgico mínimamente invasivo en el que se inserta un artroscopio, un instrumento tubular con cámara y luz, a través de una pequeña incisión para identificar y remover tejido no viable y cuerpos extraños dentro de la articulación del codo.

Liberación del túnel cubital (descompresión del nervio cubital)
El síndrome del túnel cubital es una condición caracterizada por la compresión del nervio cubital en un área del codo llamada túnel cubital. El nervio cubital recorre la parte posterior del codo detrás de una prominencia ósea llamada epicóndilo medial y pasa a través de un pasaje llamado túnel cubital.

Liberación Endoscópica del Túnel Cubital
Endoscopic cubital tunnel release is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to decompress the ulnar nerve for the treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome. Endoscopic refers to the surgery being performed utilizing an endoscope - a thin, flexible fiber-optic tube with a camera, light, magnifying lens, and a port to pass tiny surgical instruments.

Cirugía Abierta de Codo
Procedimiento quirúrgico para tratar condiciones del codo mediante una incisión grande en la piel con bisturí. Cortando tejidos grasos y capas musculares se expone toda el área operativa para que el cirujano vea completamente las estructuras afectadas.

Cirugía de Reducción Abierta de la Cabeza Radial para Reparar Fracturas de Codo
La reducción abierta y fijación interna (ORIF) de la cabeza radial es una técnica quirúrgica para tratar fracturas de la cabeza radial del codo. La ORIF de la cabeza radial restaura la anatomía normal y mejora el rango de movimiento y la función al remover la cabeza radial y reemplazarla con una prótesis (conocida como reemplazo de la cabeza radial).

Reparación del Origen del Tendón Extensor Común
El tendón extensor común es una banda dura de tejido conectivo fibroso que se adhiere al epicóndilo lateral del húmero en el codo. La ruptura o desgarro de este tendón es la lesión aguda más común del codo. La patología más frecuente es la epicondilitis, caracterizada por pérdida de la estructura normal del tendón.

Reparación de Tendones y Ligamentos del Codo
El codo es una articulación compleja del miembro superior formada por la articulación del hueso largo del brazo o húmero y los dos huesos del antebrazo, a saber, radio y cúbito. Es una de las articulaciones importantes del miembro superior y está involucrada en movimientos básicos como flexión y extensión del miembro superior y rotación del antebrazo.

Reconstrucción de Fractura de Codo
La reconstrucción de fractura de codo es un procedimiento quirúrgico para reparar y restaurar un codo dañado por trauma o lesión severa. Este procedimiento puede incluir la reparación de estructuras dañadas, o reemplazo de estructuras faltantes o dañadas con piel, músculos, ligamentos, tendones, huesos o nervios adyacentes.

Transposición del Nervio Cubital
El nervio cubital es uno de los 3 principales nervios del brazo que viaja desde el cuello a través de una protuberancia ósea en el interior del codo (epicóndilo medial), bajo los músculos del antebrazo y hacia la mano en el lado de la palma, hacia el dedo meñique.

Liberación del Nervio Cubital
La liberación del nervio cubital, también conocida como descompresión del nervio cubital, es un procedimiento quirúrgico para tratar una condición médica llamada atrapamiento del nervio cubital o síndrome del túnel cubital.

ORIF de Fracturas del Húmero Distal
Una fractura del húmero distal ocurre cuando hay una ruptura en el extremo inferior del hueso del húmero, comúnmente por trauma severo. Esta fractura puede afectar el movimiento y función del brazo, así como el trabajo y actividades diarias. Las fracturas del húmero distal son comunes y ocurren en personas de todas las edades, desde niños hasta ancianos.

ORIF de Fracturas del Olécranon
Ocurre cuando hay una ruptura en la punta ósea del codo que sobresale al mover el brazo. Puede ser extremadamente dolorosa y dificultar o impedir el movimiento del codo. Generalmente ocurre de manera aislada.

ORIF de Fracturas del Coronoides
Las fracturas de la coronoides son una ruptura en el proceso coronoides de la ulna debido a trauma o lesión. Una fractura coronoides de la ulna es una fractura intraarticular compleja que es difícil de exponer debido a las complejas estructuras anatómicas circundantes.

ORIF de Fractura de Húmero Proximal
Para ayudar a discutir la cirugía de reconstrucción ORIF como opción de tratamiento para su fractura proximal de húmero con su cirujano ortopédico, aquí hay un desglose del procedimiento quirúrgico.

Cirugía de No Unión (Codo)
Es una operación para restaurar un hueso fracturado del codo que no ha sanado incluso tras tratamiento adecuado.

Reparación del Ligamento Colateral Cubital (UCL) con Refuerzo Interno
La reparación del UCL con un refuerzo interno es una cirugía que implica el uso de una cinta recubierta de colágeno (refuerzo interno) colocada quirúrgicamente en el sitio de los ligamentos UCL dañados. Proporciona mayor resistencia y una recuperación más rápida en comparación con la cirugía de reconstrucción tradicional que implica el uso de tejido injertado del propio cuerpo.
